In an era where environmental impact is more discernible than ever, businesses must leverage available technologies to maintain sustainability.
Within the supply chain sector, particularly in produce shipping, this integration can ascertain economic efficiency while reducing carbon footprint.
Whether it’s through packaging innovations or renewable energy sources, these solutions are essential.
Today, we explore some of these cutting-edge technologies characterizing the future of this industry.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into how each of these technologies works and why they are critical.
We’ll also highlight some of the leading companies making significant strides in this arena.
Contents
- Sustainable Technologies For The Future Of Produce Shipping
- 1. Electric-powered delivery trucks
- 2. Solar-paneled transportation vessels
- 3. Cold Chain System Advancements
- 4. Bio-based Insulated Packaging
- 5. Reusable Shipping Containers.
- 6. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Ships
- 7. GPS for Efficient Route Planning
- 8. AI-Driven Logistics Management
- 9. Use of Biodegradable Materials
- 10. Aquaponic and hydroponic distribution systems
- The Bottom Line
Sustainable Technologies For The Future Of Produce Shipping
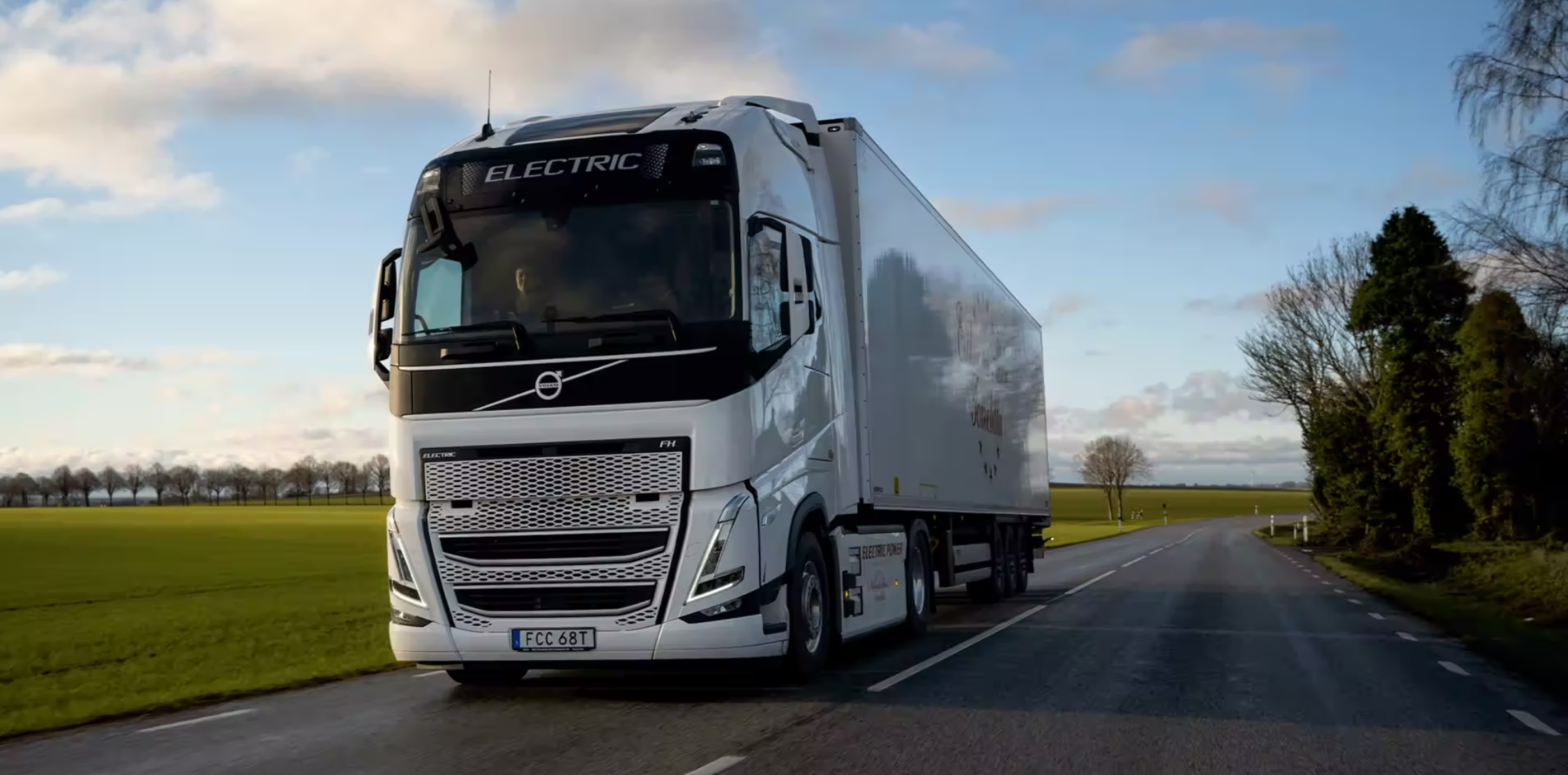
1. Electric-powered delivery trucks
Electric-powered delivery trucks are an innovative addition to the transport industry.
They offer a sustainable and efficient solution for the distribution of produce.
Unlike traditional trucks, their operation doesn’t rely on fossil fuels, which significantly reduces harmful emissions.
Electric trucks are powered by batteries, which can be recharged using renewable energy sources.
These characteristics make them ideal for the goal of achieving zero-emissions in the logistics industry.
Further, their engines are generally quieter than those of conventional trucks, contributing to noise pollution reduction.
What makes electric-powered delivery trucks stand out is their energy efficiency and their potential to reduce the carbon footprint of delivery services.
As electric vehicle technology continues to improve, the advantages of these trucks over their diesel counterparts will further increase.
There are also cost benefits involved with using electric trucks, as the cost of electricity is usually less volatile than that of fossil fuels.
Their maintenance costs are usually lower since these vehicles have fewer moving parts than their fossil fuel counterparts.
However, there are a few challenges that need to be overcome for the widespread adoption of electric trucks, such as the limited range they have on a single charge and the lack of charging infrastructure.
Significant efforts are being made by various stakeholders in the industry to develop solutions for these challenges.
A future where the transportation of produce is dominated by electric-powered delivery trucks is both plausible and desirable, considering the environmental and economic benefits they offer.
Nonetheless, transitioning from conventional delivery trucks to electric ones needs to be done strategically to ensure minimal disruptions to the supply chain while maximizing benefits.
This evolution of the transportation industry is an integral part of the broader push for green and sustainable practices in all sectors of the economy.
Moving forward, stakeholder collaboration and technology advancements will play key roles in realizing the potential of electric-powered delivery trucks in produce shipping.
2. Solar-paneled transportation vessels
The advent and continuous development of solar energy technology is revolutionizing the future of produce shipping.
The use of solar panels in transportation vessels is a viable option for maximising renewable energy and promoting sustainable practices.
The shipping industry is a major consumer of fossil fuels, with harmful emission levels posing a threat to the environment.
Amid this reality, the necessity for solar-paneled transportation vessels cannot be overemphasized.
Adding solar panels to vessels can significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels thus contributing to a cleaner environment.
Advanced solar panels can be integrated into marine vessels to produce energy, thereby reducing the dependence on diesel-powered engines.
These solar panels can also be used to power the onboard electronics and the cooling systems of these vessels, especially those used for shipping produce.
By doing so, refrigeration units in shipping components can be adequately powered, without relying on traditional carbon-based options.
Solar energy has many benefits, among which are cost-efficiency and sustainability.
Costs associated with fuel purchase and maintenance can be significantly reduced by integrating solar systems in vessels.
Also, solar energy is plentiful and is free to capture, it is an eco-friendly power source with no carbon emissions, and it does not contribute to global warming.
Moreover, solar panels require minimal maintenance, making them economically viable options for shipping companies.
Investment in solar energy technologies can also stimulate economic growth through the creation of green jobs and investment in research and innovation for more efficient systems.
While solar energy might not be the absolute solution for all marine vessels, their contribution to carbon footprint reduction is substantially rewarding.
Given the rapid advancement in technology, the ability of solar energy to power marine vessels will continue to grow exponentially.
The shift towards renewable energy sources, such as solar power, is, therefore, not only necessary for the environment, but also beneficial for the economy in the long run.
3. Cold Chain System Advancements
The modern era has seen tremendous advancements in the cold chain system, especially with a growing focus on sustainability.
It’s now possible to optimize the temperature of refrigerated cargo, ensuring that produce remains fresh during transit.
Major advancements in thermal insulation have also played a key role in enhancing the efficiency of cold chain systems.
Companies are now using phase change materials (PCMs) to maintain stable temperatures despite fluctuating external conditions.
This has proved to be a vital tool for transporting perishable products such as fruits, vegetables, and meat, in all weather conditions.
Even more impressive, real-time temperature monitoring systems have become a standard feature in cold chain logistics.
This feature allows for immediate intervention if a problem arises, minimizing food waste and sustaining quality.
Also, these monitoring systems have been integrated with advanced analytics, offering insights that can lead to further improvements in cold chain processes.
For instance, they can predict potential equipment failures before they occur, therefore averting losses and contamination.
These technological advancements have come with cost-effective measures that make cold chain processes economical for producers.
They have also reduced energy consumption , making these processes less harmful to the environment.
Moving forward, the focus is shifting towards developing micro cold chain systems for transportation over shorter distances.
These are customized for low-cost, electric-powered distribution vehicles, designed specifically for last-mile delivery.
These innovations are extending the life of produce, decreasing waste, and enhancing the efficiency of global food supply chains.
As sustainability takes center stage in industries worldwide, the role of cold chain system advancements in the shipping and logistics sector cannot be overstated.
The continuous improvement in cold chain systems will undeniably play a crucial role in shaping the sustainability of produce transportation in the future.
4. Bio-based Insulated Packaging
The use of bio-based insulated packaging has proven to be a game-changer in the field of produce shipping.
This type of packaging is typically crafted from renewable resources, reducing the dependency on fossil fuels and limiting the emission of harmful greenhouse gases.
What is commendable about these bio-based materials is that they pose no harm to the environment even when they deteriorate over time.
With bio-based insulation, there is a significant decrease in the amount of waste reaching the landfill as it’s both renewable and often compostable.
The use of this innovative packaging results in a lower carbon footprint, making it a sustainable choice for transporting various perishable items.
These materials also provide excellent thermal insulation, which is essential to maintain the freshness of produce during long shipping journeys.
The use of bio-based packaging has ensured extended shelf life for fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and many other perishable items.
Many manufacturers are considering the switch to bio-based insulated packaging to reduce their impact on the environment and meet consumer demands for sustainable practices.
It is predicted that the widespread use of bio-based materials could result in significant cost savings in the long run, considering the economic penalties often associated with traditional, non-sustainable packaging materials.
Not only does it reduce environmental harm, but bio-based packaging can also improve brand image as consumers are increasingly seeking out companies that prioritize sustainable practices.
The use of this innovative packaging technology is growing, with many new bio-based materials being developed to meet the needs of different types of produce.
Despite its many benefits, there are some challenges associated with bio-based packaging like production scalability and the need for wider commercial acceptance.
However, with continuous research and technological advancement, these challenges can be overcome, paving the way for bio-based insulated packaging to become the standard in the produce shipping industry.
Opting for bio-based insulated packaging is a win-win situation for both the planet and the produce shipping industry.
5. Reusable Shipping Containers.
One of the emerging sustainable technologies being implemented in the shipping of produce is the use of reusable shipping containers.
This move is part of the wider effort to reduce waste and minimize environmental impact in the logistics sector.
Reusable shipping containers are designed with high-grade, durable materials that can withstand repeated use over long periods.
They can easily be cleaned and sterilized, thereby ensuring the safety and quality of the produce being transported.
A significant benefit of reusable shipping containers is the reduction in the demand for single-use packaging, such as cardboard boxes or plastic crates.
By simply choosing to reuse, companies can significantly cut down on their carbon footprint and reinforce their commitment to sustainability.
This is not just an environmentally responsible decision, but also a strategic move that can benefit businesses financially.
The initial investment in reusable shipping containers may be high, but, over time, it can prove more economical than constantly purchasing disposable packaging.
Not only does this result in cost savings, but it also encourages organizations to think more competently about resource management, and to design systems that optimize the use and reuse of materials.
From a waste management perspective, the use of reusable shipping containers can greatly reduce the burden on landfills and waste treatment facilities.
Moreover, it can help conserve resources like trees and petroleum, which are commonly used in the production of single-use packaging materials.
Furthermore, shipping containers can be designed to be stackable and collapsible, optimizing space usage in storage and transportation, and thereby contributing to fuel efficiency.
Importantly, the implementation of reusable shipping containers must be complemented by the development and enforcement of responsible disposals and collection systems to ensure effectiveness.
Considerations should also be given to the design of containers for efficient cleaning and the use of eco-friendly cleaning agents.
Ultimately, it is imperative to continue exploring innovative strategies and technologies like reusable shipping containers, to ensure sustainable produce shipping now and in the future.
6. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Ships
As technology continues to evolve, so does the importance of eco-friendly transportation methods, such as hydrogen fuel cell ships.
These unique vessels function on the principle of hydrogen fuel cells, which are essentially large batteries that generate electricity through chemical reactions.
Unlike conventional fuel-run ships, hydrogen fuel cell ships do not emit carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants and hence, they are increasingly seen as a sustainable shipping option for the future.
Central to the operation of hydrogen fuel cell ships is the fuel cell system, which utilizes hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to produce electrical power, with water and heat as its only byproducts.
This process results in zero-emission maritime transport, providing a cleaner, more sustainable form of shipping.
Moreover, these ships have demonstrated that they can function as effectively as traditional vessels but with much less environmental impact.
The use of hydrogen fuel cells in ships also allows for installation flexibility, quiet operation, and potential for high energy efficiency.
Many shipping companies are exploring the potential benefits of this technology to make significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions from their operations.
However, the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in shipping also comes with its share of challenges.
These include concerns about the safety and storage of hydrogen, the cost and availability of green hydrogen, as well as infrastructural and regulatory issues.
Despite these obstacles, continuous advancements in hydrogen fuel cell technology are expected to mitigate these challenges and make this form of transportation more viable in the future.
Studies and pilots are underway exploring the integration of hydrogen fuel cells in various types of vessels, from small passenger ferries to large cargo ships – demonstrating the versatility of this technology.
With increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the shipping sector, investments in hydrogen fuel cell technology are likely to increase, leading to more innovative developments and commercial applications.
The transition to hydrogen fuel cell ships is not just a possibility, but a necessity for a sustainable and eco-friendly future in produce shipping.
By combining these technological advancements with other sustainable practices, the shipping industry can ensure a greener and more sustainable environment for generations to come.
7. GPS for Efficient Route Planning
Advancements in technology have brought about powerful tools like Global Positioning System (GPS), significantly improving the efficiency of produce shipping.
GPS, when integrated with transportation systems, greatly optimizes route planning and decision-making processes.
As a consequence, sustainable technologies like GPS lower transportation costs, reduce emissions, and enhance the overall performance of produce shipping operations.
Modern GPS devices have real-time tracking features, significantly aiding in quick decision making.
These systems help in monitoring the progress of the delivery trucks in real-time, thereby helping minimize delays and ensuring timely deliveries.
Moreover, tracking transportation through GPS helps in anticipating and mitigating any potential disruptions caused by traffic snarls or adverse weather conditions.
Through constant monitoring, this sustainable technology can enhance route efficiency by suggesting the most optimal and least congested routes.
By providing data on current traffic conditions, GPS significantly helps in avoiding high traffic zones and thus, reducing the transit time.
Reducing transit time not only ensures freshness of the produce but also reduces the carbon footprint due to reduced fuel consumption.
The benefit is twofold – it reduces the negative impact on the environment and also increases the profitability of the produce shipping industry due to reduced fuel usage.
Ensuring freshness of produce is of utmost importance in the produce shipping industry and with the help of GPS technology, the transit time can be controlled and minimized.
GPS also provides accurate prediction of delivery times, allowing businesses to better manage their supply chain and inventories.
With these relevant predictions, businesses can avoid overstocking or understocking, thereby reducing wastage and ensuring customer satisfaction.
GPS integrated data can also be used for analytical purposes, to further improve the overall efficiency of the produce shipping processes.
Data-driven insights can help reveal patterns and trends, and identify areas of improvement in the shipping routes and schedules.
Thus, GPS, when effectively used in the shipping processes, serves as a crucial sustainable technology – driving significant cost savings, reducing carbon emissions, and ensuring the timely delivery of fresh produce.
8. AI-Driven Logistics Management
When we contemplate the future of sustainable technologies within the realm of produce shipping, a critical component that undoubtedly presents itself in the foreground is AI-driven logistics management.
As global consumerism rises, the need for enabling forceful, reliable, and effective distribution networks has never been more urgent.
Fortunately, the advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) can equip us with the indispensable tools we need to pave a greener path forward.
Specifically designed to aprend, adapt, and optimise, AI promises significant advancements within the area of logistics management.
By predicting and adapting to impending changes, AI-based systems have the potential to vastly improve efficiency, reduce waste, mitigate environmental impact and thus lead to a significant advancement in sustainability.
This is primarily accomplished by enabling real-time tracking and visibility of every asset within the supply chain.
For instance, through AI-driven forecasting, organizations can predict demand patterns, enabling them to adjust supply volumes accordingly, thereby minimizing waste.
Advanced AI algorithms can also optimise transportation routes leading to less fuel usage and reduced carbon emissions – a vital aspect when considering sustainable technologies.
The role AI plays in logistics, particularly within precise tracking and predictive analytics, has a profound impact on resource management and contributes significantly to the objective of achieving greener operations.
Furthermore, AI-driven logistics can lead to improved life cycle assessment of a product from cultivation or manufacturing to disposal, including transportation and packaging phases – an essential aspect of sustainability.
Technologies like AI and IoT also introduce the potential for autonomous vehicles, capable of revolutionizing the shipping industry, by enabling operations to continue twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, without fatigue.
These capabilities provided by AI are significantly more efficient and reliable, thereby directly resulting in reduced carbon footprints and minimized environmental impact.
In the context of sustainable distribution of produce, AI-driven logistics could lead to the drastically reduced need for preservatives and other harmful chemicals often utilized to extend the shelf life of products.
By optimizing delivery times through machine learning, fresh produce can be delivered quicker and more efficiently, without the need for harmful chemicals; thus, sustainability can be significantly improved.
Considering these factors, it is unequivocal that incorporating AI in logistics management is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future for produce shipping.
9. Use of Biodegradable Materials
The use of biodegradable materials in produce shipping presents a promising step towards sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Biodegradable materials can break down naturally in the environment without leaving harmful residues.
In the realm of produce shipping, utilizing biodegradable materials for packaging is quickly becoming popular.
The use of bio-based polymers, plant starch, and other natural substances have begun replacing plastic and styrofoam in packaging materials.
Considering the tremendous waste produced by traditional packaging materials, the switch to biodegradable materials can significantly mitigate the environmental impact of produce shipping.
For instance, biodegradable peanuts made from cornstarch are already in use, replacing traditional polystyrene peanuts.
Furthermore, companies like Mushroom Packaging are utilizing mushroom mycelium to make packaging materials that can break down in a garden within weeks.
Additionally, bioplastics derived from plants like corn and sugarcane are being used to make produce bags and containers that are compostable.
These innovations in biodegradable materials improve overall sustainability in the supply chain by minimizing waste and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Besides packaging, the utilization of biodegradable pallet wraps, netting, and adhesive tapes is on the rise, contributing to environmentally friendly shipping practices.
The introduction of biodegradable insulating materials, like wool and paper insulation, are also being implemented to maintain fresh produce’s temperature throughout transportation.
The successful implementation of biodegradable materials in produce shipping begins with commitment from companies to invest in and adopt these sustainable practices.
While the capital investment might be greater initially, the long-term savings and environmental benefits make the use of biodegradable materials a viable and valuable investment for the future of produce shipping.
The use of biodegradable materials is just one of the sustainable technologies being utilized for the future of produce shipping.
As more companies embrace these materials, we can expect a positive shift towards a more sustainable, less wasteful produce shipping industry.
10. Aquaponic and hydroponic distribution systems
In the realm of sustainable technologies, a growing edge in produce shipping is the integration of aquaponic and hydroponic distribution systems.
These innovative systems utilize water-based methods of crop cultivation to maximize efficiency and reduce the overall environmental impact associated with traditional farming and shipping practices.
Nutrient-rich water, which originates from fish waste, is utilized in aquaponic systems to fertilize crops, creating a symbiotic relationship between the marine life and the plant crops.
On the other hand, hydroponic systems eliminate the need for soil altogether by directly supplying plants’ roots with nutrient solutions.
The produce grown using these systems often exhibit enhanced growth rates and superior quality compared to their counterparts grown in more traditional settings.
By leveraging aquaponic and hydroponic methodologies, we can essentially create local, virtually self-sustaining ecosystems that drastically reduce the need for long-distance shipping and its associated emissions.
Moreover, these systems do not require the use of chemical pesticides since they are housed in controlled environments, which further lowers their environmental impact.
Such systems, if integrated into urban environments like buildings or city lots, would allow for fresh, local produce to be grown and distributed within the very communities that will consume them.
This promises not only quality enhancement but also the possibility of significant reductions in carbon emissions produced by long-haul produce transportation.
The agricultural waste from these systems can also be upcycled and used within the same distribution network, contributing to a zero-waste circulation process.
These facts make aquaponics and hydroponics a desirable option for cities seeking to decrease their carbon footprint while providing fresh, locally grown produce to their residents.
Aquaponic and hydroponic distribution systems are, without a doubt, a promising solution to the challenges of sustainable produce shipping, but wide-scale adoption is not without challenges.
Adopting these systems on a large scale requires significant investment due to high setup costs and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
Despite these challenges, the long-term environmental and social benefits of aquaponic and hydroponic systems serve as significant incentives for their incorporation within the realm of sustainability-focused produce shipping.
The increasing demand for locally grown, high-quality produce, together with the paramount need to reduce carbon emissions, provides a strong impetus to explore these innovative systems further.
The Bottom Line
From electric-powered delivery trucks to AI-driven logistics management, the novel trends in sustainable shipping are evidently transforming the industry.
Such groundbreaking technologies promise not only environmental protection but are also increasingly cost-effective, promising immense economic benefits.
Also, the move towards biodegradable materials and renewable energy sources like solar and hydrogen fuel cell are significant steps towards Earth conservation.
Furthermore, advancements in cold chain systems and innovative distribution methods such as aquaponic and hydroponic systems underscore novel ways to reduce waste and in turn, carbon footprint.
Thus, it’s evident that striving for sustainability in shipping and logistics is not only feasible but invariably crucial for the longevity of the industry and the well-being of our planet.